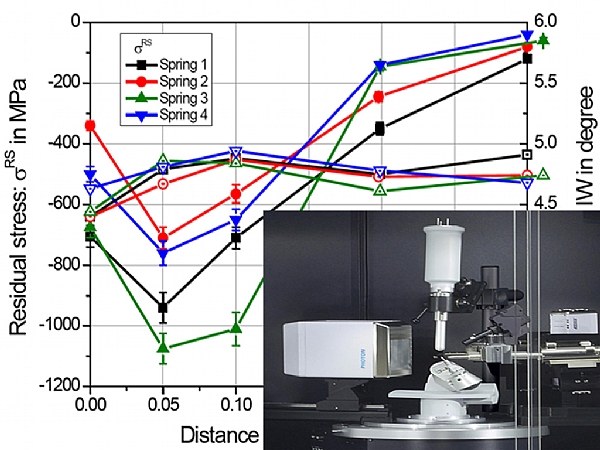
X-Ray Measurements
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is the most accurate method for quantifying residual stress due various mechanical treatments such as bending, coiling, grinding, chamfering, shot peening, etc. XRD is a method in which the residual stress in a material is calculated from the strain in the crystal lattice. XRD used to quantify the residual stress as a function of depth up to 300 micron below the surface, with high resolution due to the shallow penetration of the x-ray beam. XRD techniques are well established, having been standardized and developed by both the SAE and the ASTM.